Personal Loan
Debt Consolidation vs. Debt Settlement: What's the Difference?
EXPECTED READ TIME:6 MINUTES
Each year, eliminating debt is one of the top financial goals for Americans. There are several strategies to manage and reduce debt. We’re going to explain the differences between two of them — debt consolidation vs. debt settlement — and which is right for you.
What Is Debt Consolidation?
Debt consolidation is the practice of combining multiple high-interest debts into a single debt with one monthly payment. Four of the most common forms of debt consolidation include:
- Debt consolidation personal loan
- Debt management plan
- Balance transfer
- Student loan program
People managing multiple, high-interest debts, such as credit cards or student loan payments may find this approach helpful.
Benefits of Debt Consolidation
Consolidating your debt can simplify your bill-paying system — with some potential benefits.
- With all your debts merged into one loan, you’ll be making one monthly payment instead of many.
- You may have a lower monthly payment and a lower interest rate.
- You can choose an option with a fixed rate so there are no surprise rate hikes.
Debt consolidation is the practice of combining multiple high-interest debts into a single debt with one monthly payment.
Drawbacks of Debt Consolidation
With the perks come the pauses, so take some time to think about the disadvantages of debt consolidation before moving forward.
- Although a lower monthly payment is a plus, it can draw out your payment schedule, meaning you may pay more over time.
- You have to qualify for debt consolidation loans and balance transfers.
- Debt management services may charge initial and monthly fees.
Consolidating your debt can simplify your bill-paying into one monthly payment.
How Does Debt Consolidation Affect Your Credit Score?
As a general rule, taking out a debt consolidation loan will require a hard credit inquiry, meaning your credit score will temporarily decrease by a small amount.
However, consolidating debt can drastically improve your credit score in the long run, assuming you make your payments consistently and don’t add more debt in the meantime.
Here’s how different options may impact your credit:
- Personal loan: Requires a hard inquiry on your credit, which initially decreases your score, but can have long-term benefits to your credit score.
- Home equity loan/HELOC: Each requires a hard credit inquiry that initially reduces your credit score. But again, if you don’t miss payments, this method will benefit your credit in the long run.
- Balance transfer: Like other forms of consolidation, opening a new credit card to transfer your balance to would result in a hard inquiry on your credit, but making your payments on time will cause your score to gradually rise.
- Student loan debt consolidation: Because this requires getting a new loan to consolidate your other loans into, this would also require a hard credit inquiry. But when it comes to your credit score, the positives of paying down your debt far outweigh the small hit your score takes when you take out a loan.
While debt consolidation reduces the number of monthly bills you pay, debt settlement aims to lower the amount of debt you owe.
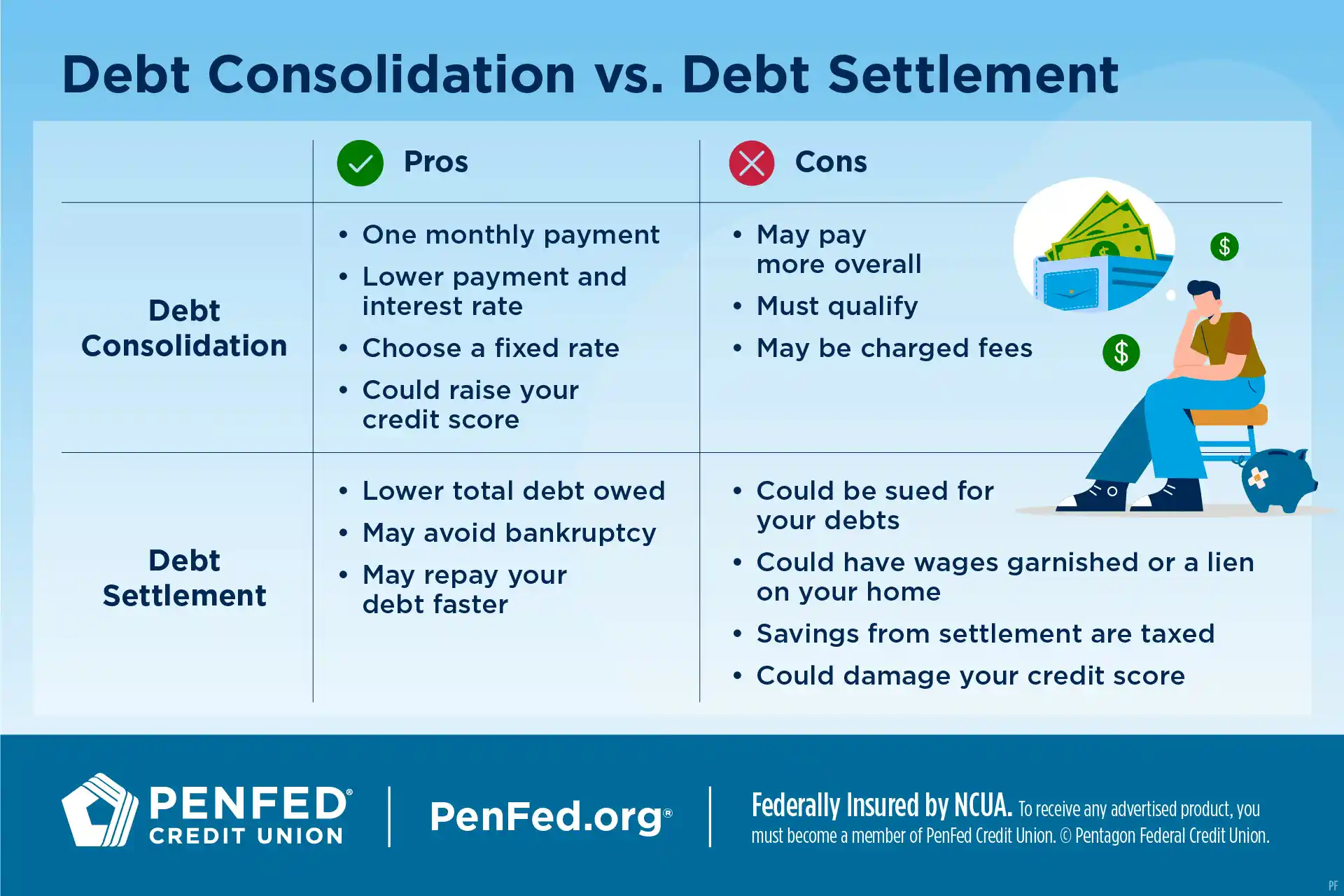
Pros & Cons of Debt Consolidation
Do the benefits of debt consolidation outweigh the risks? Let’s compare them:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
One monthly payment |
May pay for a longer time and pay more over time |
|
Potentially lower monthly payment and interest rate |
Must qualify |
|
Can choose a fixed rate — no surprise rate hikes |
Debt management services may charge fees |
|
Can raise your credit score in the long run |
|
Credit Inquiries
Hard inquiries are done after you apply for credit and can lower your credit score by up to five points. Soft inquiries, such as checking your own credit, do not affect your score.
What Is Debt Settlement?
Debt settlement is a completely different approach to managing your debt. While debt consolidation reduces the number of monthly bills you pay, debt settlement aims to lower the amount of debt you owe.
With debt settlement, a for-profit company works with your creditors to negotiate a settlement for you to pay, which is a lump sum that’s less than what you actually owe. People who might otherwise go bankrupt because of their financial situation might consider debt settlement.
Generally, a debt settlement company will suggest that you stop making monthly payments to your creditors and instead make monthly payments to an escrow-like account. Most often, the debt settlement company will set up and manage the account and charge you fees for those services.
You should plan on taking 3-4 years to grow enough savings to pay off your settlement. Don’t forget that in the meantime, your debts will continue to accrue interest and late fees.
You should plan on taking 3-4 years to grow enough savings to pay off your settlement.
Benefits of Debt Settlement
Debt settlement may potentially help certain consumers, but the advantages aren’t guaranteed. Here are some of the possible benefits:
- If a negotiation is reached with your creditors, it may lower the amount of debt you owe.
- It may help you avoid bankruptcy. But not all creditors are willing to work with debt settlement companies, so you’ll need to make sure your creditors are willing to before proceeding.
- Depending on the negotiations with your creditors, debt settlement may help you repay your debt in less time than it may have taken you otherwise.
Drawbacks of Debt Settlement
On the surface, debt settlement may seem appealing (who doesn’t want to pay less debt?), but there are risks to consider.
- If you stop payments to your creditors, you may potentially be sued for repayment. Creditors can garnish your wages or put a lien on your home if they win a lawsuit.
- Any savings from debt settlement can be considered taxable income, so you may have to pay income taxes on the forgiven debt.
- Your credit score and credit report will likely be damaged.
Pros & Cons of Debt Settlement
Not sure which is right for you? Here are some risks and benefits to consider:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
May lower the amount of debt you owe |
Potentially could be sued for debts |
|
May help you avoid bankruptcy |
Could have your wages garnished a lien placed on your home |
|
Maybe help you repay your debt faster |
Savings from debt settlement are taxable income |
|
|
Likely damage your credit score |
How Does Debt Settlement Affect Your Credit Score?
Debt settlement ultimately hurts both your credit score and credit report. Here’s why:
- Withholding payments from your creditors will negatively affect your credit score.
- Creditors that don’t receive payment may sell your debts to collection agencies, which can result in negative credit report entries that will remain for seven years.
- Settling your debt means you won’t pay the full amount you owe. This will also stay on your credit report history for seven years, which can make it more difficult to get credit in the future.
Knowing your credit score can help you move forward with tackling your debt.
On the surface, debt settlement may seem appealing, but ultimately it hurts both your credit score and credit report.
Which Approach Is Best for You?
You have options as you work toward your goal of getting debt-free. To recap debt consolidation vs. debt settlement:
- Debt consolidation is aimed to help people pay down multiple, high-interest debts, such as student loans or credit card debt.
- Debt settlement may appeal more to those who might otherwise go bankrupt.
Remember to consider how each option may affect your credit score and credit report. Taking these steps now can help you stay on track with your goals and improve your financial future.
The Takeaway
Paying off debt is never easy, but understanding your options is a good first step. Choose a financial tool that matches your situation and start regaining your financial freedom.
Want to Consolidate Your Debt?
Find out how much a debt consolidation loan can help you lower your interest rate and monthly payments.




